Commit to Lifelong Learning
"perpetuam uitae doctrina!"
"Live as if you were to die tomorrow.
Learn as if you were to live forever." Mahatma Gandhi.

Your Brain Matters. Take Care of it!
Lifelong Learning Nurtures Your Brain.
You need your brain for learning and learning nurtures your brain.
The human brain is an incredibly complex and fascinating organ. It is the most important and powerful organ in the human body and its functions are essential for our everyday lives.
With so many different parts of the brain, it can be difficult to understand how they all work together.
In this article, we will go over the different parts of the brain, what they do, and why they are so important.
Read on, to learn a bit more
about the parts of the human brain.
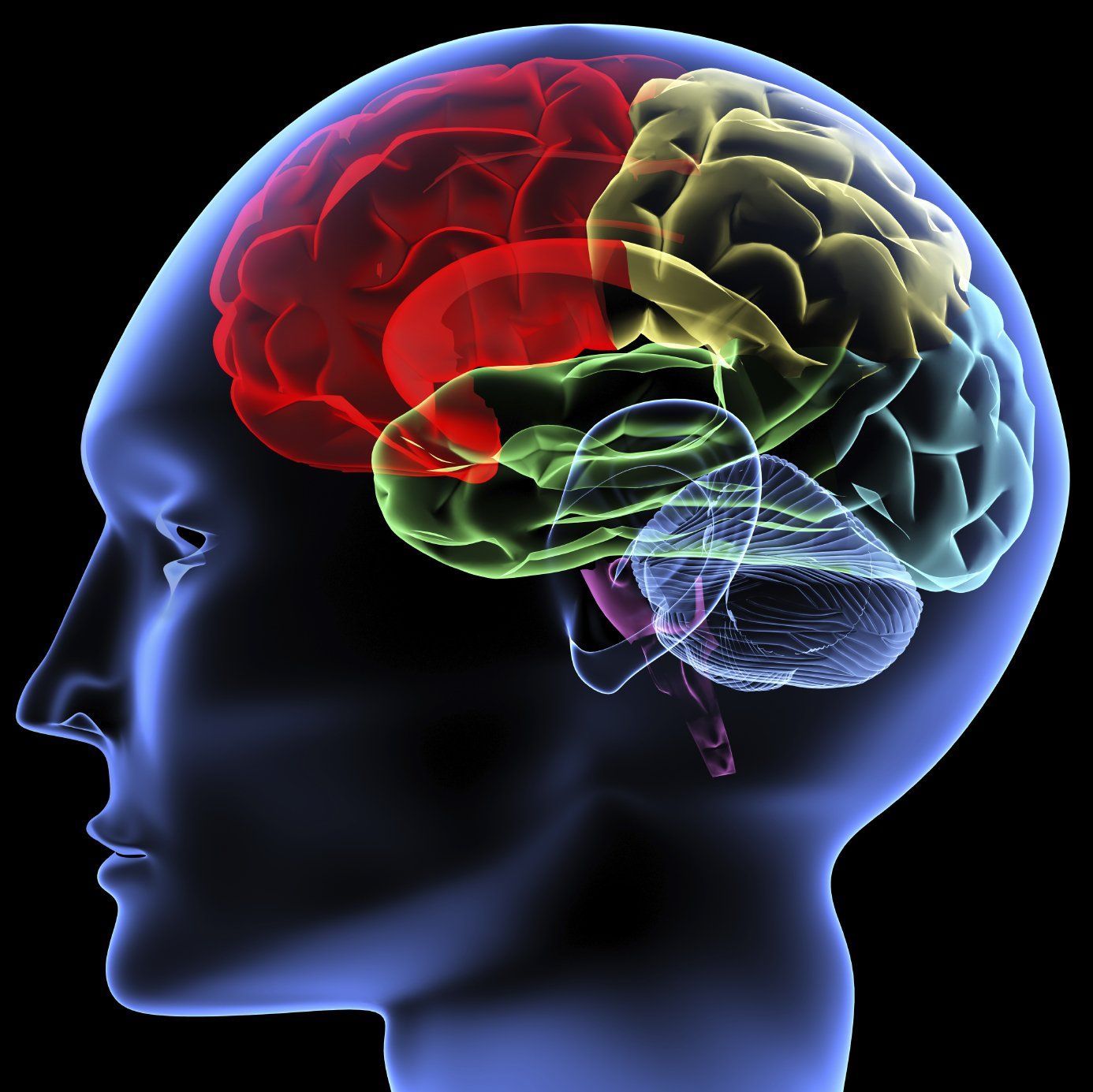
The Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest and most complex part of the human brain. It is divided into two sections, the left and right hemispheres, each of which is further divided into four lobes: the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes.
The cerebrum is responsible for higher functions such as problem solving, memory, speech, emotions, planning, judgment, and motor control. It is also responsible for interpreting sensory input from the eyes and ears and for controlling voluntary body movements such as walking.
The outer layer of the cerebrum is called the cerebral cortex and is made up of millions of nerve cells. This layer is responsible for interpreting incoming information and executing complex functions.
The cerebrum controls the activities that enable us to think and reason, helping us make decisions and solve problems. It is also responsible for our ability to learn and store information, as well as allowing us to recognize faces and understand language.
How Does the Human Brain Work?
Have you ever wondered how the human brain works? What makes us think, remember, and move?
For centuries, scientists have been attempting to answer these questions and finally, the mysteries of the human brain are being revealed.
In this article, we will take a deep dive into the fascinating world of neuroscience and explore how the brain works.
Join us as we explore the intricate pathways of the human brain and uncover its secrets!
How the Brain Processes Information
When we think, talk or move, our brain is hard at work. But how does it do all of these things? The answer lies in understanding how the brain processes information.
The human brain is made up of millions of neurons, or nerve cells, that communicate with each other to help us carry out our daily tasks. Neurons have three main parts: a cell body, an axon and dendrites. These parts act like electrical switches, allowing them to send and receive signals from one another.
When we experience something, our neurons fire off electrical signals in response. This information is then sent through the axon, which carries the signal to other neurons in the brain. The dendrites on the other neurons receive the signal and if enough neurons are stimulated, a new signal is sent off. This process is known as neurotransmission and it’s how the brain processes and stores information.
This is just a basic overview of how the brain works. But as we continue to learn more about the inner workings of the brain, we’re gaining a better understanding of how it processes information and why certain behaviors occur.
Sponsored
Seven Tips for Keeping Your Brain Healthy as You Age
As we age, our brain health becomes increasingly important. With age, comes the increased risk of developing dementia and other cognitive impairments. But there are simple steps you can take to maintain your brain health and reduce the chances of developing these impairments. In this article, we will discuss seven tips for keeping your brain healthy as you age, to help you stay sharp and functioning at your best!
List of Services
-
1. Get regular exerciseList Item 1
Exercise is essential for keeping your brain healthy as you age. Regular exercise can improve learning and memory, delay cognitive decline, and even help prevent Alzheimer's disease and dementia.
Exercise is also a great way to reduce stress, which can lead to improved brain health. Not only that, but it helps create new brain cells, helping to keep your mind sharp and your memory intact.
-
2. Eat a healthy dietList Item 2
Good nutrition is an important part of maintaining good brain health.
Eating a healthy diet can help keep your memory sharp, reduce cognitive decline and even prevent diseases like Alzheimer's and dementia.
A balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, proteins and fats is the best way to ensure your brain has the fuel it needs for a happy life.
-
3. Don't smokeList Item 3
Smoking has long been linked to a number of serious health problems, including heart disease, cancer, and stroke. But did you know that smoking is also associated with cognitive decline and memory loss?
Smoking increases your risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and dementia, which can drastically reduce quality of life in later years.
-
4. Reduce stressList Item 4
Stress is one of the most important factors in maintaining your brain health as you age.
When we are stressed, our body releases hormones that can damage the brain over time and lead to memory loss and cognitive decline.
-
5. Get enough sleep
One of the most important things you can do to ensure a healthy brain is to get enough sleep.
Research has shown that getting enough quality sleep is essential for good memory and cognitive health. Lack of sleep can increase your risk of developing memory loss, Alzheimer's disease, and dementia.
-
6. Limit alcohol consumption
Alcohol consumption should be limited to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
Excessive drinking has been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline, memory loss, and an increased risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and dementia.
-
7. Stimulate your mind
Staying mentally active is one of the most important ways to keep your brain healthy.
A good memory and the ability to think clearly are essential for leading a happy life.
We all know that our brains are capable of incredible things, but what you might not know is that your brain can actually physically change itself. This process is called brain plasticity, and it means that our brains can adapt and change in order to accommodate new experiences and learnings.
In this article, we'll explore what brain plasticity is, how it works, and the ways it can be used to help us learn and grow. We'll also discuss the potential risks associated with brain plasticity and the importance of understanding how our brains are wired.

1). What is Brain Plasticity?
Brain plasticity, also known as neuroplasticity, refers to the brain's ability to adapt and change throughout one's life. It is the brain's ability to modify its neural pathways and connections in response to experiences, environmental stimuli, and learning.
For a long time, it was believed that the brain stopped developing after childhood. However, recent research has shown that the brain continues to change and adapt throughout our lives, with the ability to create new connections and neural pathways.
This ability of the brain to adapt is critical for our learning and development, as well as for our recovery from injuries, strokes, and other brain-related disorders. Understanding the concept of brain plasticity is essential to appreciate how the brain works, how we learn, and how we can improve our brain health.
In summary, brain plasticity is the brain's ability to change and adapt in response to experiences, stimuli, and learning, leading to the formation of new neural connections and pathways.

2). The Science behind Brain Plasticity
Brain plasticity, also known as neuroplasticity, refers to the brain's ability to reorganize itself in response to changes in the environment, learning, or experience. This phenomenon occurs throughout the lifespan, from infancy to adulthood.
At the cellular level, brain plasticity is mediated by the complex interactions between neurons and the connections they form. Neurons communicate with one another through synapses, which are the sites where signals are transmitted from one neuron to another. When two neurons are frequently activated together, their synapses become strengthened, a process known as synaptic potentiation. Conversely, when neurons are not activated together, their synapses weaken or even disappear, a process known as synaptic depression.
These synaptic changes can lead to modifications in brain circuits, which are collections of interconnected neurons that work together to perform specific functions, such as vision, hearing, memory, and movement. For example, if someone practices playing the piano every day, the brain circuits that control finger movements, hand-eye coordination, and auditory perception will become more efficient and interconnected.
Brain plasticity is also influenced by various molecular and genetic factors. For instance, the production of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, can enhance or suppress brain plasticity. Moreover, certain genes are involved in regulating the growth and survival of neurons and the formation of synapses, which can affect brain plasticity.
In addition to learning and experience, brain plasticity can be induced by brain injury, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or neurodegenerative diseases. In these cases, the brain may compensate for the lost or damaged functions by recruiting other brain areas or by forming new connections.
Overall, brain plasticity is a complex and dynamic process that underlies many aspects of human behavior and cognition. Understanding the mechanisms of brain plasticity may have important implications for the development of therapies for neurological and psychiatric disorders, as well as for the enhancement of cognitive and motor skills.
Protect Yourself from EMF Radiation

As we travel along on our lifelong-learning journey, we need to pay attention to our overall health. We need to nurture our body, mind and spirit. A grave and silent threat to our health is the Electromagnetic Field radiation emitted by the many electronic devices that we use.
EMF radiation, or Electromagnetic Field radiation, is a type of radiation that is emitted by electronic devices, including cell phones, laptops, and tablets. This type of radiation is also present in the environment, and can be produced by power lines, radio waves, and other sources. While some types of EMF radiation, such as visible light and radio waves, are not harmful to humans, others, such as those emitted by cell phones, can pose significant health risks.
In recent years, the number of electronic devices that we use on a daily basis has increased significantly. While these devices provide many benefits, they also expose us to high levels of EMF radiation. This exposure can lead to a range of health problems, including headaches, fatigue, among other things.
In order to protect ourselves from the dangers of EMF radiation, it is important to understand what it is, how it affects our bodies, and how we can reduce our exposure to it. By taking proactive steps to shield ourselves from this harmful radiation, we can reduce our risk of developing serious health problems in the future.
Let’s take a more in-depth look into this subject and how the
EMFDEFENSE Anti-radiation shield can help protect you.




Research and Resources
Brain Plasticity(Neuroplasticity)
According to Psychology Today, brain plasticity, or neuroplasticity, refers to the human brain's ability to change and adapt in response to life experiences. This brain quality is extremely important to all mankind. The brain's ability to wire and re-wire itself (plasticity) explains why some older adults are able to thrive cognitively; or why some people with brain damage recover a great deal of their cognitive prowess (with therapy).
Brain plasticity supports the following statements:
- The human brain does not stop growing after a certain age.
- You can teach an old dog new tricks.
- Cognitive decline is not inevitable as we age.
- Your brain can recover from damage.
Source: brainHQ.
Brain-related Resources
The Cleveland Clinic:
Johns Hopkins Medicine:
"Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works."
WikipediA:
The Mayfield Clinic:
The Mayo Clinic:
"Slide Show: How the Brain Works"
National Institutes of Health (NIH):
NIH: National Library of Medicine:
"Information about the Brain."
"Neuroanatomy, Cerebral Hemisphere"
More Resources on Neuroplasticity
The National Library of Medicine
- The Impact of Studying Brain Plasticity
- Neuroplasticity
- Brain plasticity and behavior in the developing brain
- Dynamic Brains and the Changing Rules of Neuroplasticity: Implications for Learning and Recovery
- The aging mind: neuroplasticity in response to cognitive training
- Role of Lifestyle in Neuroplasticity and Neurogenesis in an Aging Brain
- Exercising Your Brain: A Review of Human Brain Plasticity and Training-Induced Learning
PaychCentral
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
- MIT scientists discover fundamental rule of brain plasticity
- Study reveals how, when a synapse strengthens, its neighbors weaken.